2. Effect of cosolvents
When designing and experimenting with formulas to increase the speed of ink drying, we found that the addition of certain co-solvents not only improves the initial drying but also reduces the viscosity of the system. Therefore, isopropyl alcohol, which is commonly used in industry and easily available, was selected as a co-solvent, and the effect of the cosolvent on the viscosity of the ink was examined through experiments. Surfactant A2 and a mixture of A2 and isopropanol were used as controls. The experimental procedure and method were the same as above.
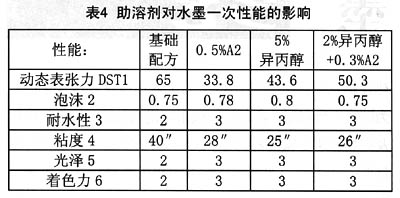
From the experimental test results shown in Table 4, it can be seen that the use of alcohol alone or a mixture of A2 and A2 can greatly reduce the surface tension and achieve similar performance, that is, 5% of isopropyl alcohol reduces surface tension and improves wetting. Both the performance and the printing film performance are equivalent to 0.5 wt% of A2, and defects such as pits are not found. Provides room for cost reduction. As a result, the wetting agent may be partially used in the ink system for prints that do not require high VOCs (organic volatiles).
3. Effect of Aminating Reagent on Ink Viscosity
The amination process of the ink resin can be seen from FIG.

During the printing process, as the volatilization of aminating reagents results in a drop in the pH of the ink, we know that a drop in pH will lead to an increase in the viscosity of the ink system and the instability of the ink system. It can be seen from the experimental results in FIG. 3 that the viscosity of the R1 resin is drastically increased at a pH of 8.5 or less by ammoxidation of the R1 resin. Although a newly developed neutral pH product is now reported, this product changes the pH-sensitive characteristics of the existing standard alkali-soluble polymer, and the neutral pH product does not use excess ammonia to dissolve the resin. The most suitable pH range of application From 6.5 to 7.2, this type of resin is currently not widely commercialized and is not available in the country. Since the stability of the pH directly affects the viscosity and viscosity stability of the ink, we have further investigated the influence of the aminating reagent on the pH value and viscosity stability of the ink system.

The amination reagents with different properties are listed in Table 5 and their base neutralizing ability was determined. As can be seen, the use of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol in the formulation requires less ammonia and monoethanolamine. Since ammonia is relatively weakly alkaline and more volatile, the pH stability of the ink when using ammonia as an aminating agent is poor, thereby further affecting the stability of the viscosity of the ink system.

Figure 4 compares the change in pH during storage for two months at high temperatures using an aminating ink system with three aminating agents. As can be seen from the figure, 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (curve 1) is superior to monoethanolamine (curve 2), monoethanolamine is superior to aqueous ammonia (curve 3), and the pH of the aqueous ammonia system is increased. From 9.2 to 7.4; while adding 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol and monoethanolamine pH is still not less than 8.0.

At the same time, in the dispersive grinding test, it was also found that with the progress of dispersion, the pH stability of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol and monoethanolamine is higher than that of ammonia water; in addition, the high ammonia consumption also brings The corrosion of the barrels and other issues. For printing on porous substrates, the use of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol or monoethanolamine does not negatively affect drying time and water resistance due to the water absorption properties of the porous surface of the paper, taking into account both cost and performance ( Odor, dryness, and plasticity. In order to obtain a stable viscosity ink system, a mixture of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol or monoethanolamine and 28% aqueous ammonia may be selected as the neutralization alkalinity. Resin amination reagents. In order to provide the ink with the best overall performance, another recommended method is to use 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol in the preparation of the colorant and to use ammonia when diluting.
Third, the conclusion
The above experiments show that the highly efficient aqueous wetting and dispersing agent and co-solvent can greatly reduce the surface tension of the aqueous system and then reduce the viscosity of the system. In addition, the amination agent plays an important role in the viscosity change and the viscosity of the ink system. Therefore, it provides an important theoretical basis for designing a high solid and low viscosity ink formulation system and obtaining an ideal ink application viscosity. (Text/Fang Hongxia Chen Guoping Jiang Zhen)
Edge Control,Instant Edge Control,Curl Mousse For Frizz Control,Edge Control Gel For Black Hair
DELIN HAIR COSMETICS , https://www.hairdyecolorfactory.com